Green Anaconda
Eunectes murinus
-
 Green Anaconda
Green Anaconda -

-

-

-

-

About the Green Anaconda

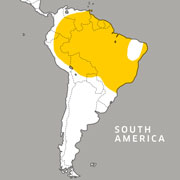
Geographic Range:
Class: Reptilia
Order: Squamata
Family: Boidae
Genus: Eunectes
Species: murinus
The green anaconda is dark green with oval patches on its back and smaller spots with yellow centers on its side. This coloring camouflages it in the wet, dense vegetation of its rainforest habitat. The green anaconda is not venomous, though it does have sharp teeth and powerful jaws to clench prey, which it then pulls underwater and drowns. Anacondas prefer to be in the water, where they can remain submerged for 10 minutes.
Anaconda Facts
Appearance:
Dark green in color with black oval patches on the back. The sides have smaller spots with yellow centers.
Size:
Length: Males, approximately 9 feet; females, approximately 15 feet (females are much larger in adulthood than males). Mature snakes can average up to 16 feet in length.
Weight: Averages 350 to 550 pounds
Diet:
Large rodents, tapirs, capybaras, deer, peccaries, fish, turtles, birds, sheep, dogs and aquatic reptiles. Younger anacondas feed on mice, rats, chicks, frogs and fish.
Reproduction:
Anacondas have no specific breeding season. Mating occurs in the water. After carrying the eggs in her body for six months, the female gives birth to 20-40 live young on average. Rarely up to 100 offspring are born. Maturity is usually based on size rather than age, and size is dependent on prey availability and genetics. Males become mature when they've grown to about 6 feet long and females when they've grown to about 9 feet long.
Behavior:
Green anaconda spend the majority of their time in water to help offset their bulk. Their eyes and nostrils are located on the tops of their heads, allowing them to see and breathe while remaining mostly submerged and hidden. Their spots help them blend in with the pattern of lights created by the forest canopy. They're not venomous so they constrict their prey. They will also drag prey into the water to drown it. The green anaconda consumes its prey whole and digests the bone and fur along with the meat. This means that they can go weeks or even months without feeding while they digest their previous meal.
Habitat/Range:
Tropical rainforests, swamps, and marshes. Anaconda can be found throughout tropical South America, mainly in the Amazon and Orinoco Basins.
Median Life Expectancy:
10 years
Threats:
Likely habitat loss threatens the anaconda.
You Can Find This Animal in the Tropical Forest
A sensational swimmer
Excellent swimmers, anacondas use the shallow waters of streams and rivers to escape predators.
At Franklin Park Zoo:
At Stone Zoo:








